What Is a CRM in Marketing: How to Use CRM to Drive Leads, AI Personalization, and Better Ads
Discover what is a CRM in marketing and how to use CRM to generate leads, automate campaigns, sync Meta and TikTok ads, and deploy AI chat agents for growth.
Jan 6, 2026

Every modern marketer needs a system that turns customer data into predictable growth. A CRM in marketing centralizes contact records, tracks behavior, automates personalized campaigns, and ties online advertising to real revenue. This guide explains what is a CRM in marketing, how it improves lead generation and ad performance, and a practical 30-60-90 day plan to get results.
What is a CRM in marketing?
A CRM in marketing is a software platform that stores customer and prospect data and powers marketing actions based on that data. It is both a database and an engine. The database holds contact details, interaction history, purchase records, and behavioral signals. The engine uses that data to segment audiences, trigger emails, run personalized advertising, score leads, and report on campaign performance.
People often confuse CRM platforms with marketing automation tools. They overlap. A CRM in marketing should integrate deeply with marketing automation features. In many modern platforms the two are part of the same product. The real value comes when you can follow a contact from first click to long term customer and understand where marketing drives revenue.
Why the question what is a crm in marketing matters is simple. Without a CRM marketers work from incomplete data. With a CRM marketing becomes measurable, repeatable, and scalable.
Why CRM matters for modern marketing
CRM marketing turns scattered touchpoints into a single source of truth. That matters for these outcomes:
Personalization at scale. Use browsing history, past purchases, and ad interactions to tailor messages that convert.
Better lead quality. Automated lead scoring surfaces the contacts most likely to buy so sales follows up faster.
More efficient paid media. Sync CRM segments with Meta and TikTok to create high value custom and lookalike audiences.
Higher retention and lifetime value. Timely reengagement and cross-sell campaigns keep customers longer.
Aligned teams. Sales, marketing, and customer success share the same data and handoffs.
CRM also unlocks advanced use cases such as predictive churn scoring and AI-powered content recommendations. When CRM data feeds AI models you can automate next-best-action suggestions for every user.
Key features of CRM marketing platforms

A capable CRM for marketing includes these core features:
Centralized contact profiles. Full history of interactions, purchases, preferences, and consent status.
Segmentation and audiences. Build dynamic segments based on behavior, lifecycle stage, value, and custom fields.
Marketing automation and workflows. Triggered emails, SMS, push notifications, and workflow branches.
Lead scoring and routing. Score leads by engagement and route hot leads to sales or an AI chat agent.
Multi-channel campaign management. Orchestrate email, social, SMS, in-app, and ad campaigns from the same platform.
Analytics and attribution. Track conversions, lifetime value, cohort performance, and channel ROAS.
Integrations and APIs. Connect to ad platforms, e-commerce, analytics, helpdesk, and chatbots.
AI and predictive tools. Predictive lead scoring, content recommendations, and automated copy or subject line suggestions.
Mobile-first features. Mobile-optimized campaigns and SMS or in-app messaging capabilities.
Practical examples include automatically adding people who visit a pricing page to a nurture sequence, sending an SMS if an email is unopened, and exporting a segment to Meta for a retargeting audience. Many CRMs now allow direct partnerships or connectors to Meta and TikTok ad platforms for near real time sync.
For a deep dive on AI chat integration see Automated AI Chat Agents - The Social Search.
How CRM improves lead generation and paid ads performance
CRM makes lead generation measurable and repeatable. Use cases marketers rely on:
Capture and qualify. Capture leads from forms, chat, social, and ads. Use scoring to qualify before sales outreach.
Retarget and nurture. Move cold traffic into nurture funnels with context aware messaging.
Sync segments to ads. Export high intent segments to Meta and TikTok to build lookalike audiences and lower acquisition costs.
Closed loop attribution. Match ad spend to actual revenue using CRM order and LTV data.
Example flow: you run a TikTok video ad to drive signups. The CRM tags new leads from that ad with the campaign UTM and begins a welcome workflow. After three engagements the CRM scores the lead and automatically pushes high scorers to a sales queue or to a messenger-based AI chat agent.
To operationalize paid media with CRM you need clean tracking, event mapping, and a connector or middleware that syncs audiences in both directions. If you run paid campaigns consider combining CRM-driven creative testing with the recommendations in our Paid Ads Management - The Social Search resource.
30-60-90 day implementation roadmap
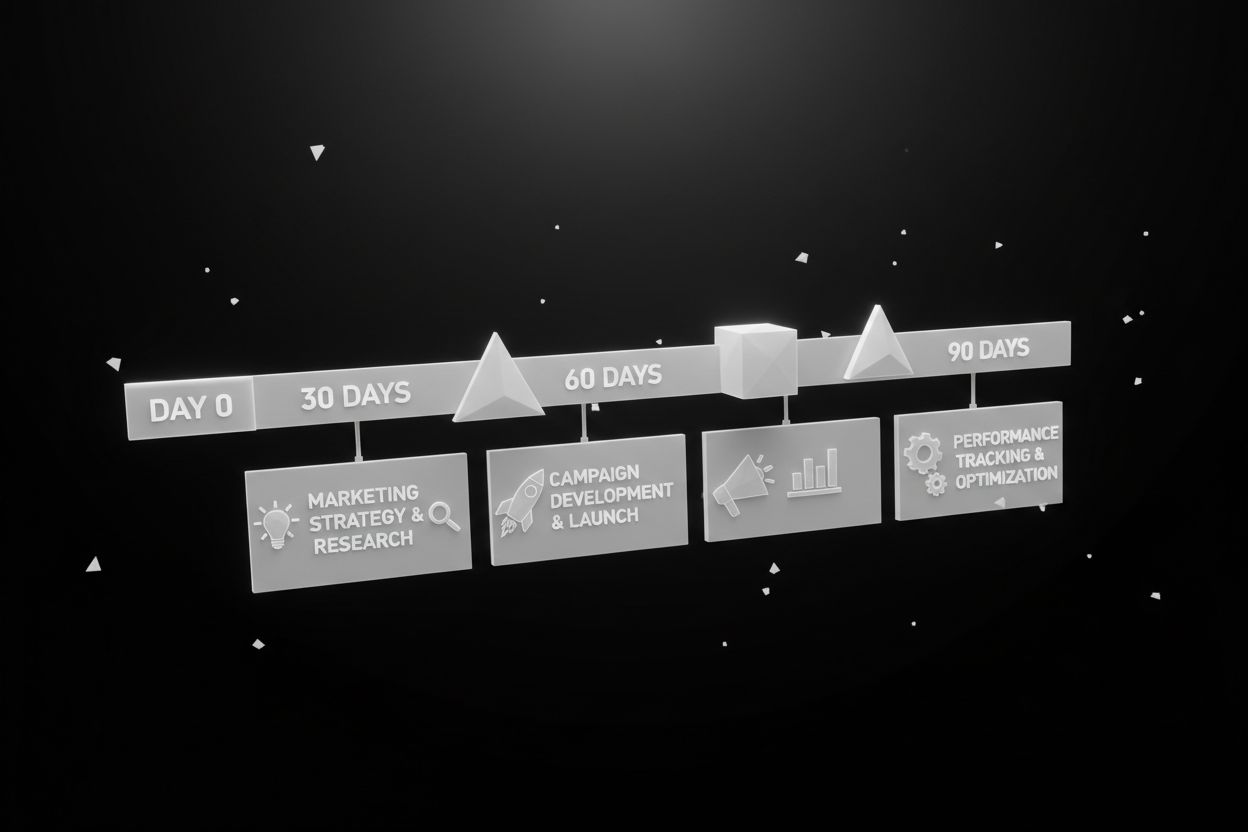
This practical roadmap focuses on revenue outcomes and adoption.
Days 1-30 - Audit and foundation
Define business goals and target KPIs like CAC, conversion rate, and CLV.
Audit your data sources. Map where contact and transaction data lives today.
Clean your data. Remove duplicates and standardize fields.
Choose a CRM platform and list required integrations.
Implement basic tracking and UTM standards.
Set up a simple welcome workflow and test form captures.
Days 31-60 - Build and activate
Create core segments for top, middle, and bottom of funnel.
Build lead scoring rules and routing logic.
Integrate with ad platforms for audience sync and automated exports.
Launch a nurture flow tied to a low friction offer.
Connect an AI chat agent to handle inbound queries and route sales leads. See how this can automate responses in Automated AI Chat Agents - The Social Search.
Start simple paid tests using CRM segments on Meta and TikTok.
Days 61-90 - Measure, optimize, and scale
Implement attribution reporting and tie revenue back to campaigns.
Optimize lead scoring thresholds and routing rules.
Automate cross-sell and reengagement sequences for existing customers.
Train teams and document processes.
Launch a pilot for advanced AI features such as predictive churn or content personalization.
For a guide on generating pipeline with automation use Automated Lead Generation - The Social Search and our Lead Generation and Marketing Automation Guide for 2026 Success - The Social Search.
Industry-specific CRM marketing use cases
CRM tactics differ by industry. Here are practical examples and KPIs.
Retail and e-commerce
Use CRM to track purchases, returns, and browsing behavior.
Run abandoned cart workflows and personalized product recommendations.
KPI targets: cart recovery rate 10-20 percent, repeat purchase rate increase 15 percent.
B2B SaaS
Track trial behavior and product usage signals for lead scoring.
Use account based marketing workflows and cross-channel outreach.
KPI targets: lead to opportunity conversion 5-15 percent, sales cycle reduction 20 percent.
Healthcare
Respect consent and privacy. Store explicit preferences and consent timestamps.
Automate appointment reminders and patient education journeys.
KPI targets: no-show reduction 30 percent, patient retention improvement 10 percent.
Local services and agencies
Combine CRM with local ad audiences for seasonal offers and retargeting.
Use SMS and chatbots for immediate booking confirmations.
KPI targets: booking conversion rate increase 12 percent.
Each industry benefits from a tailored approach to segmentation, messaging cadence, and privacy controls.
Metrics and KPIs every CRM marketer should track
Track both marketing performance and data quality.
Marketing performance
Customer acquisition cost CAC by channel
Lifetime value CLV by cohort
Lead to opportunity conversion rate
Marketing influenced revenue
Email open and click through rates
Ad ROAS and cost per lead
Data quality and operations
Percentage of contacts with valid emails and phone numbers
Duplicate rate
Time to lead response
Workflow success rate
Set baseline metrics during the first 30 days and use the 60 and 90 day checkpoints to measure progress.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Many CRM projects fail because of simple reasons. Avoid these pitfalls.
Bad data. Clean and standardize before heavy automation.
Over automation. Start with simple rules and add complexity after testing.
No ownership. Assign a CRM product owner for governance and priorities.
Ignoring privacy. Implement consent capture and storage early to avoid compliance risk.
Siloed reporting. Create shared dashboards for marketing, sales, and success.
Poor training. Provide role based training and quick reference guides.
A small amount of upfront discipline prevents rework and increases adoption.
Integrations, AI, and data privacy
Integrations
A CRM needs to connect with your tech stack. Common connectors include:
Ad platforms: Meta, TikTok, Google Ads
Email and SMS providers
E-commerce platforms and payment processors
Analytics and data warehouses
Chatbots and helpdesk systems
Use middleware or native connectors for real time audience sync. That sync is what enables campaigns that respond to recent behavior.
AI capabilities
AI can accelerate personalization and prediction. Useful AI features include:
Predictive lead scoring based on historical outcomes
Content personalization and automated subject line testing
Chatbots that use CRM context to produce smarter responses
Next best action recommendations for sales reps
Mobile CRM marketing
Design for mobile first. Many customers interact primarily on mobile through social apps and messaging. SMS, RCS, and in-app notifications should be part of your playbook.
Privacy and compliance
Comply with GDPR, CCPA, and local data rules by:
Capturing consent with timestamps and purpose
Implementing data subject request workflows
Minimizing retention and storing only necessary data
Using secure connectors and encryption
Documentation and audit trails help during compliance checks and build customer trust.
Vendor comparison and cost considerations
Vendors range from enterprise systems to lighter tools. A short comparison:
Salesforce - Highly customizable and powerful for enterprise but costly and requires significant implementation resources.
HubSpot - User friendly with integrated marketing features. Mid market friendly and quicker to launch.
Zendesk Sell - Customer service centric with CRM features and tight helpdesk integration.
Lightweight options - Many smaller CRMs offer quick setup and affordable pricing for small teams.
Cost estimate framework
Setup and migration: $3,000 to $50,000 depending on complexity
Subscription: $20 to $300 per user per month
Integrations and middleware: $50 to $2,000 per month
Ads and creative: separate line item depending on spend
Calculate ROI by modeling: increased conversion rate times average order value times expected retention lift minus total cost. Use conservative numbers and run scenario analysis.
Team structure, migration, and adoption
Who owns CRM marketing
CRM Product Owner. Owns roadmap and governance.
Marketing Ops. Builds campaigns, manages integrations, optimizes scoring.
Data Analyst. Maintains data quality and attribution models.
Sales reps. Use CRM to follow and close qualified leads.
Customer success. Runs retention and upsell campaigns.
Migration best practices
Map fields and keep a backup of legacy data.
Migrate in waves and validate at each step.
Maintain historical data for attribution where possible.
Training and adoption
Run role based training sessions and office hours.
Provide quick win templates for common campaigns.
Incentivize usage with metrics tied to performance.
FAQ
Q: How is CRM different from marketing automation?
A: CRM focuses on customer records and lifecycle. Marketing automation focuses on campaign orchestration. Modern platforms combine both.
Q: When should a company adopt CRM marketing?
A: When you have repeatable customers or a pipeline to manage and you want to tie marketing to revenue.
Q: Can CRM reduce ad costs?
A: Yes. CRM driven audiences and lookalikes often improve targeting and reduce cost per acquisition.
Q: Is CRM necessary for small businesses?
A: Small businesses can benefit from lightweight CRM to avoid lost leads and improve follow up.
Q: What is a typical time to see ROI?
A: Expect meaningful signals in 60-90 days and payback on setup within 6 to 12 months with disciplined measurement.
Q: How do I handle privacy when syncing to ad platforms?
A: Use hashed identifiers, honor consent flags, and follow platform specific data policies.
Next steps
If you want to move from planning to results start with a short audit of data and tracking. Create the first segment and run a simple nurture sequence tied to an ad test. For hands on services and support check our guides and services on automation and ads management linked throughout this article such as Automated Lead Generation - The Social Search, Automated AI Chat Agents - The Social Search, Paid Ads Management - The Social Search, Lead Generation and Marketing Automation Guide for 2026 Success - The Social Search, and Automated Social Media - The Social Search.
A CRM in marketing is not a silver bullet. It is a system that rewards discipline and curiosity. Invest in clean data, thoughtful segments, and measured experiments and the platform will compound your marketing results over time.